Cameroon: Africa in miniature
The country is called "Africa in miniature" for its high diversity of climate, culture, and geography.
Overview
| Flag |
|
| Anthem |
Ô Cameroun, Berceau de nos Ancêtres (French) |
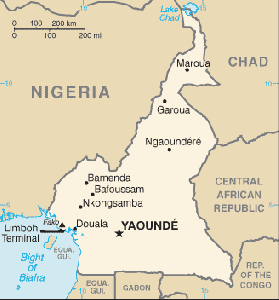
| Capital |
Yaoundé |
| Largest city |
Douala |
| Official language(s) |
French, English |
| Cameroonian |
| Government |
Republic |
| Area |
475,442 km2, 183,568 sq mi |
| Population |
~ 19 million |
| Currency |
Central African CFA franc (XAF) |
| Internet TLD |
.cm |
Geography
Cameroon is a country of central and western Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Cameroon's coastline lies on the Bight of Bonny, part of the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean.
Yaoundé is the capital of Cameroon and second largest city in the country after Douala. It lies in the centre of the nation. The population of Yaoundé city is about 1,430,000. The largest city of Cameroon, Douala, has an estimated population of 3,000,000. The third largest city of Cameroon is Garoua with 490,000 inhabitants. The city is an important river
porta place on the coast at which ships can shelter, or dock to load and unload cargo or passengers.
Society and culture
The country is well known for its native styles of music, particularly makossa and bikutsi, and for its successful national football team. Each of Cameroon's ethnic groups has its own unique cultural forms. Typical celebrations include births, deaths, plantings,
harveststhe process of gathering the ripened crop, and religious
ritualsa repeated set of actions.
Population
In 2009, Cameroon's estimated population was 19,522,000. The population is young: an estimated 40.9% are under 15, and 96.7% are under 65. Population density is highest in the large
urbanrelated to a city centres, the western highlands, and the northeastern
plainan expanse of land with relatively low relief. There are more than 230 different ethnic and linguistic groups in Cameroon, for example Sudanese, Fulani, Shuwa Arabs, Pygmies and Nigerians.
Languages
Both English and French are official languages due to the introduction of these languages during
colonialismthe time when the country was divided into colonies and ruled by other nations. A fifth of Cameroon's population in the Northwest and Southwest regions speak English. The rest of the population speaks French. Cameroonian Pidgin English is the most common
lingua francaa common language used by people of diverse backgrounds to communicate with one another, especially in the formerly British-administered territories. A mixture of English, French, and Pidgin called Camfranglais has been
gainingto increase, to acquire possession of what one did not have before popularity in urban centres.
Religion
Cameroon has a high level of religious freedom and diversity. Christians are concentrated in the southern and western regions, and Muslims
residelive in large numbers in every region but are concentrated in the north. Large cities have
significantnotable,reasonably large populations of both groups. People widely believe in
witchcraftthe practice of witches; magic or the use supernatural powers to influence or predict events.
Government and politics
Cameroon is a
unitary republicgoverned as one single unit in which the central government is supreme and any administrative divisions exercise only powers that the central government chooses to delegate. The President of Cameroon has broad,
unilateraldone by one side or party only powers to create policy, administer government agencies, command the
armed forcesthe military forces of a nation and much more. The current president is Paul Biya. Cameroon's legal system is largely based on French civil law with common law influences. Main political parties are the Cameroon People's Democratic Movement and the Social Democratic Front.
Economy
Cameroon's per-capita
GDPGross Domestic Product was estimated at US $2,300 in 2008. Major export markets include France, Italy, South Korea, Spain, and the United Kingdom.
Unemploymentthe state of having no job was estimated at 30% in 2001, and about a third of the population was living below the international
povertythe state of being poor or needy threshold of US$1.25 a day in 2009. Since the late 1980s, Cameroon has been following programmes to reduce poverty, privatise industries, and increase economic growth. Tourism is a growing sector, particularly in the coastal area of the country. Cameroon's natural resources are very well suited to agriculture. Bananas, cocoa, oil palms, rubber, and tea are mostly
cultivatedto grow plants.