Sudan
Overview
| Flag |
|
| Anthem |
نحن جند لله جند الوطن (Arabic) (We are the Soldiers of God and of Our Land) |
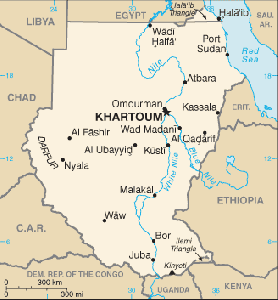
| Capital |
Khartoum |
| Largest city |
Omdurman |
| Official language(s) |
Arabic / English |
Demonyma name for a resident of a locality, often the same as the name of the people's native language
|
Sudanese |
| Government |
Federal presidential democratic republic |
| Area |
2,505,813 km2, 967,495 sq mi |
| Population |
~ 42 million |
| Currency |
Sudanese pound (SDG) |
| Internet TLD |
.sd |
Geography
Sudan is a country in northeastern Africa. It is the largest country in Africa and tenth largest in the world by area. It is bordered by Egypt to the north, Eritrea and Ethiopia to the east, Kenya and Uganda to the southeast, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west and Libya to the northwest. The world's longest river, the Nile, divides the country between east and west sides.
Sudan's capital is Khartoum with an
urbanrelated to the city population of 639,598 people. The city serves as the political, cultural and commercial centre of the nation. Omdurman remains the largest city. It has a population of around 2.4 million people.
Society and culture
Sudanese culture combines the behaviors,
practicescustomary actions; habits, and beliefs of about 578 tribes, communicating in 145 different languages. The country has geographic extremes varying from sandy
desertan area of land with little water or vegetation to tropical forest.
Population
Sudan has a population of more than 39 million people. There are 597 different
tribessocially, ethnically, and politically cohesive groups of people. One major ethnic group in Sudan are the Arabs. Sudan also hosts a
refugeea person seeking a state of safety, protection or shelter in a foreign country population. According to the World Refugee Survey 2008, 310,500 refugees lived in Sudan in 2007. The majority of this population comes from Eritrea, Chad, Ethiopia and the Central African Republic.
Languages
Sudan's official languages are Arabic and English. However, English is only spoken by educated people. The total number of languages used in Sudan is around 142. 133 are currently spoken languages and 9 languages are
extinctno longer used. The most used languages are Arabic in the north, east, west and middle regions, and tribal languages in the whole country. The
lingua francaa common language used by people of diverse backgrounds to communicate with one another in Southern Sudan is a
variantsomething that is slightly different from a type or norm of Arabic called Juba Arabic.
Religion
Three religions are dominant in Sudan: Islam, Animism and Christianity. An estimated 70% of the population
adheres toto remain fixed, either by personal union or conformity of faith, principle, or opinion Islam. The
remainderrest of the population follows either animist and
indigenousnative to an area beliefs (25%) or Christianity (5%). Islam predominates in the north, while traditional indigenous beliefs (Animism) and Christianity are dominant in the south.
Government and politics
Officially, the country is a federal presidential representative democratic republic. The President of Sudan is Head of State, Head of Government and Commander-in-Chief of the
Armed Forcesthe military forces of a nation, such as the army, navy, air force and marines in a multi-party system.
Legislative powerthe power to make a law is vested in both the government and in the two chambers, the National Assembly (Lower House) and the Council of States (Upper House). The
judiciarythe court system and judges considered collectively is independent and obtained by the Constitutional Court. However, Sudan is widely recognised as an authoritarian state where all effective political power is obtained by President Omar al-Bashir and the ruling National Congress Party (NCP).
Economy
The Sudanese economy is growing. Currently oil is the country's main export. Rich mineral resources are available in Sudan including: petroleum, natural gas, gold, silver, chromite, asbestos, zinc, iron, lead, uranium, copper, granite, nickel, tin, aluminum. Agriculture production remains Sudan's most important sector, employing 80% of the
workforceall the workers employed by a specific nation .